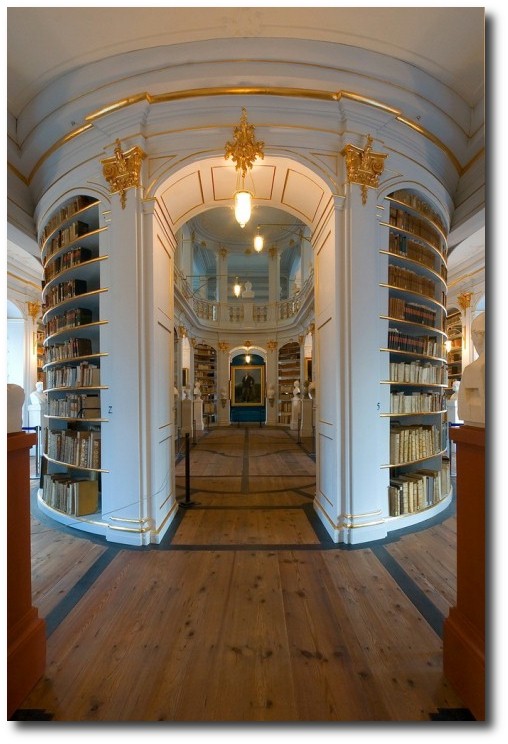
A Museum Recreates The Look Of Century Old Swedish Interiors With Historic Costumes
Picture Credit- Skansen.se
Skansen: Traditional Swedish Style – New And Used Options from $42
Founded in 1891 by Artur Hazelius, Skansen was the first open-air museum in the world; its aim to show how people lived and worked in the past in the different regions of Sweden. Hazelius was a teacher and researcher in Nordic languages who felt that traditional ways of life were disappearing with the onset of industrialization.
He started to collect an extensive collection of objects, which he put together in the form of tableau-type interiors, in a building in Drottningattan in the middle of Stockholm. Gradually, however, he wanted to show whole houses, furnished with traditional objects, furnishings and works of art, inhabited by people in historic costume, and through Skansen this idea became a reality.
Published in association with the Skansen Foundation, this beautiful book is illustrated throughout in colour. It describes not only the museum and its buildings, but also presents a microcosm of Swedish life, culture, art and architecture. The natural landscape of the museum setting is used to enhance the regional variations in Swedish art and architecture, with buildings from the southern part of Sweden being located in the southern-most part of the museum and so on.
Each chapter is devoted to a particular region represented by the museum: northern, middle and southern Sweden, as well as a typical Swedish town quarter. The buildings described here vary in date from the Vastveit storehouse, which was built in the fourteenth century, to the Skane farmstead which was finished in the 1920s. Stylistically, the range of buildings displayed at the museum is enormous: we move through time and style from the summer pasture farm, or Faboden, with its essentially medieval form of wooden construction, through the classical elegance of buildings like the late-eighteenth century Skogaholm Manor, or the impressive malm house built for the merchant Charles Tottie, to functional timber frame of the early twentieth-century Assembly Hall from Varmland. The informative, but accessible, text has been written by Ralph Edenheim, who is a Swedish art historian, and Head of the Department of Cultural History at Skansen. 128 pages.
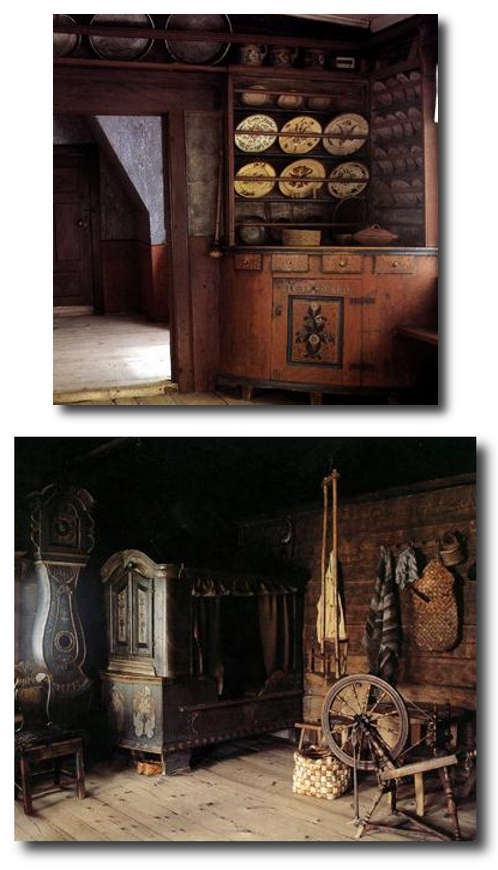
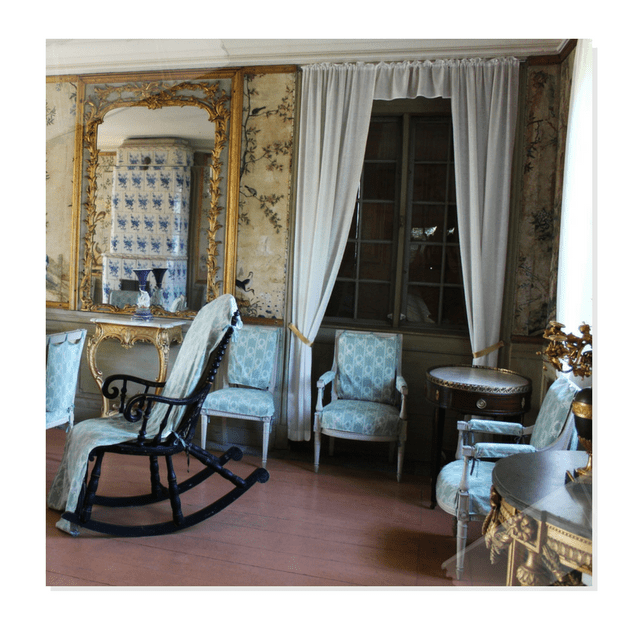
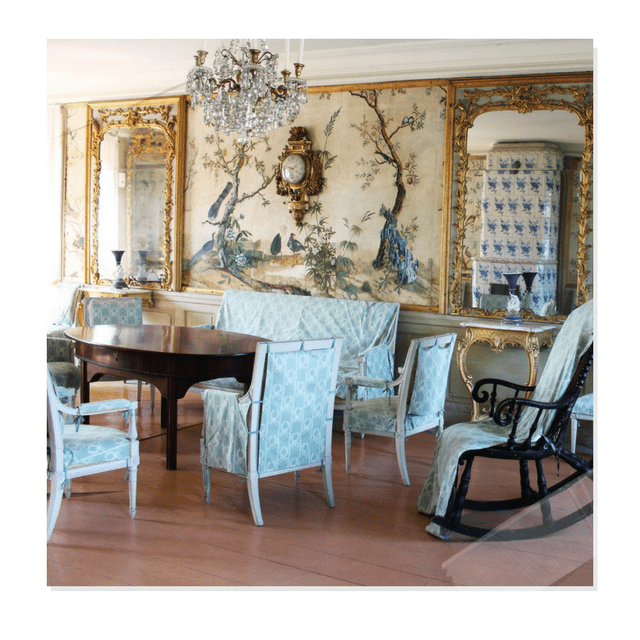
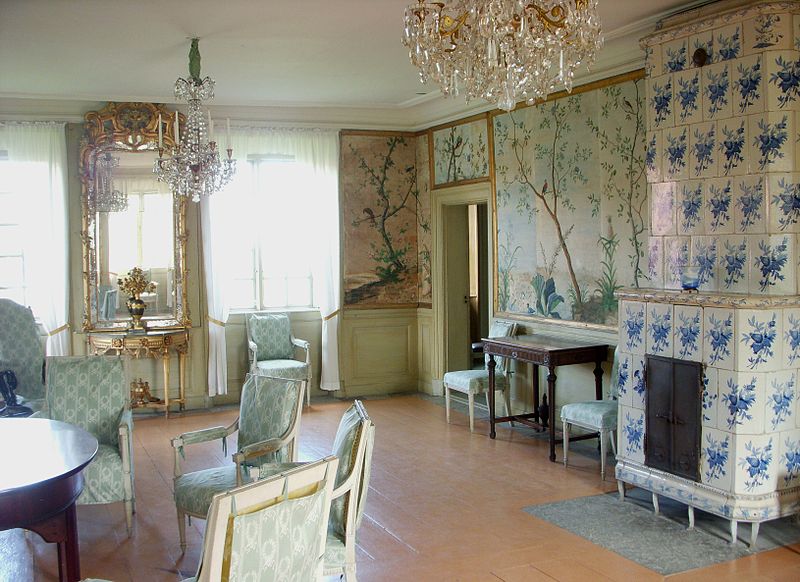
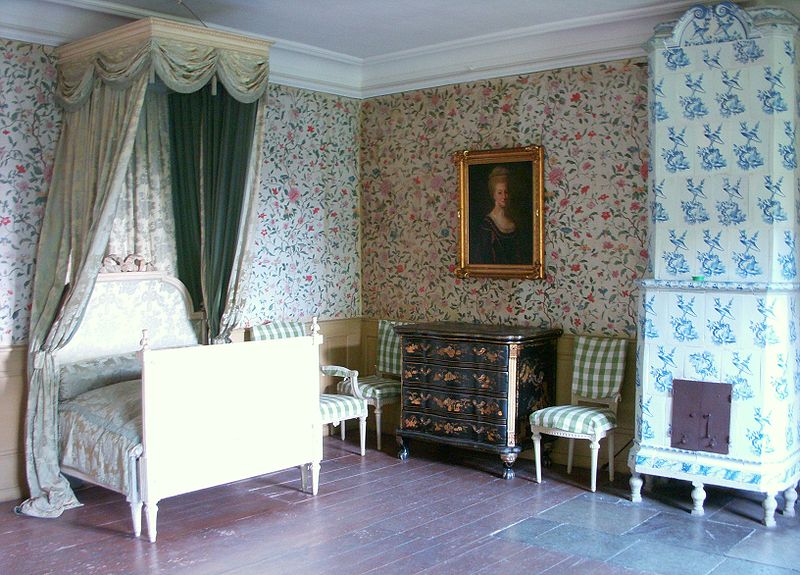
Below are pictures of Swedish Interiors are those taken from photographer Photographer Joanna Holmgren found in two publications Skansen: Traditional Swedish Style , Swedish Folk Art: All Tradition Is Change
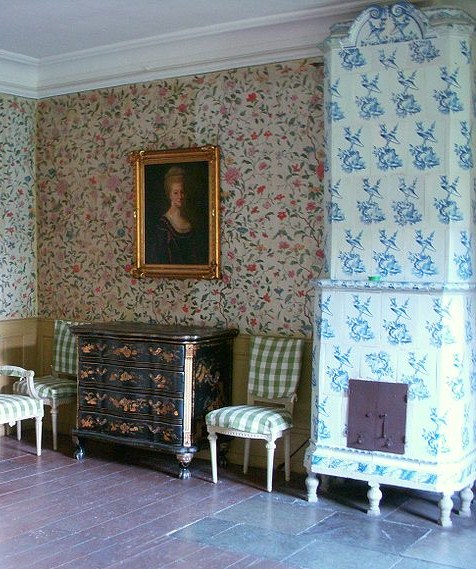
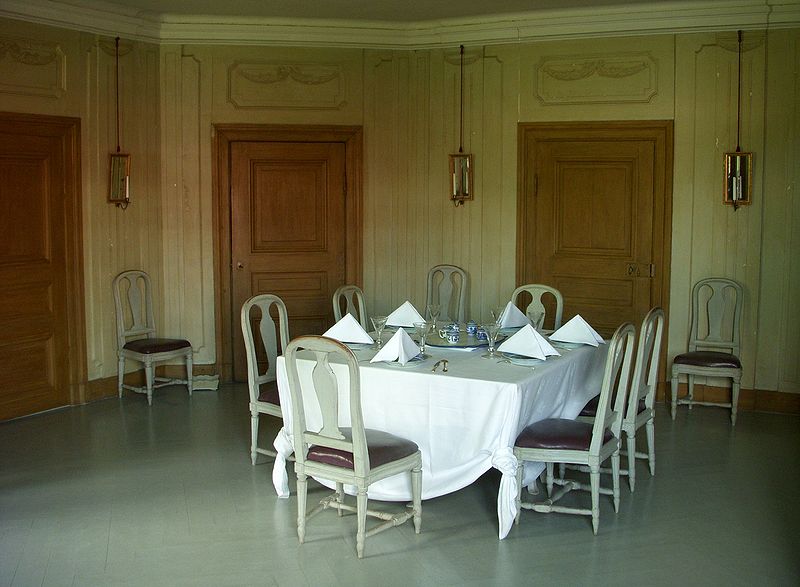
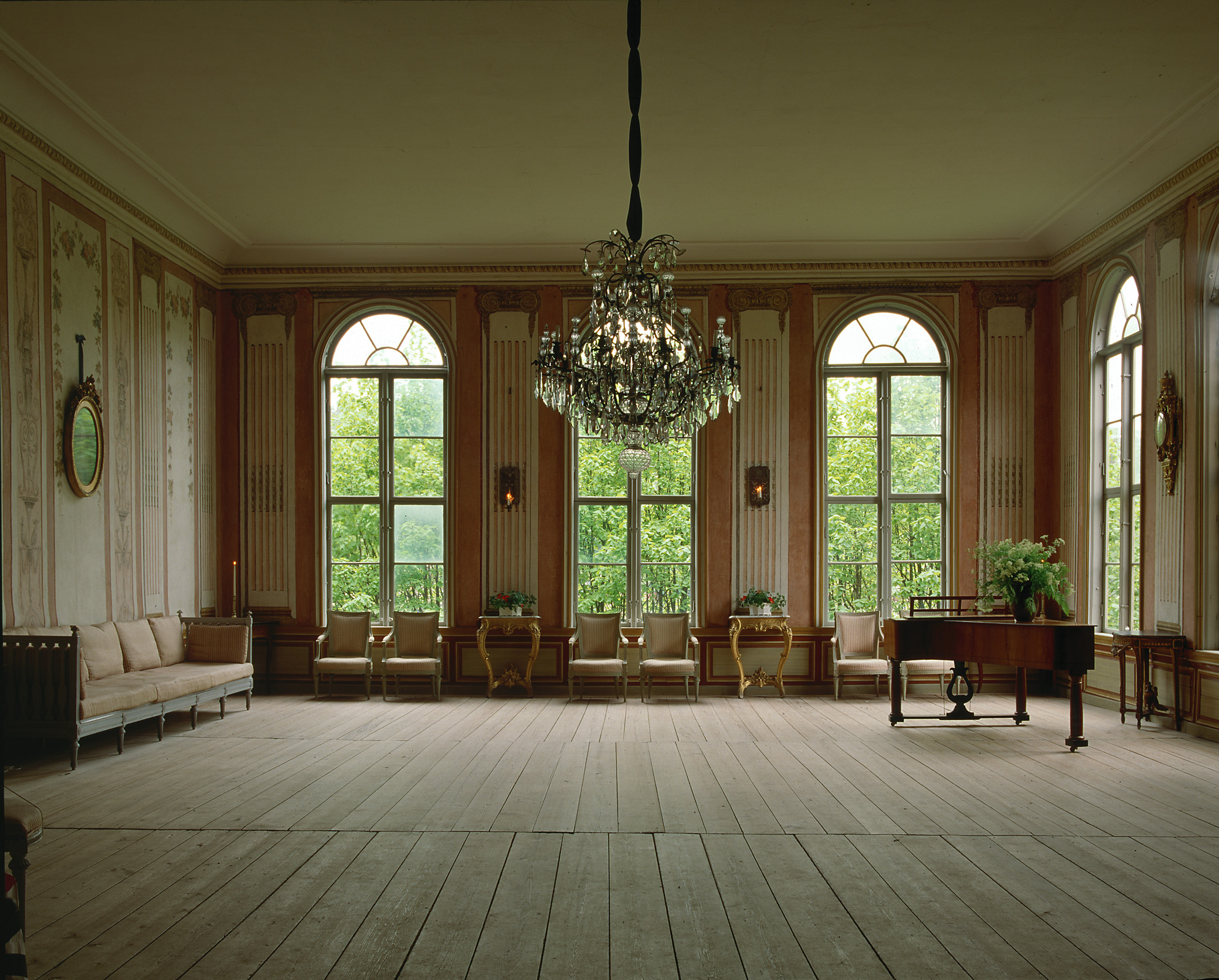
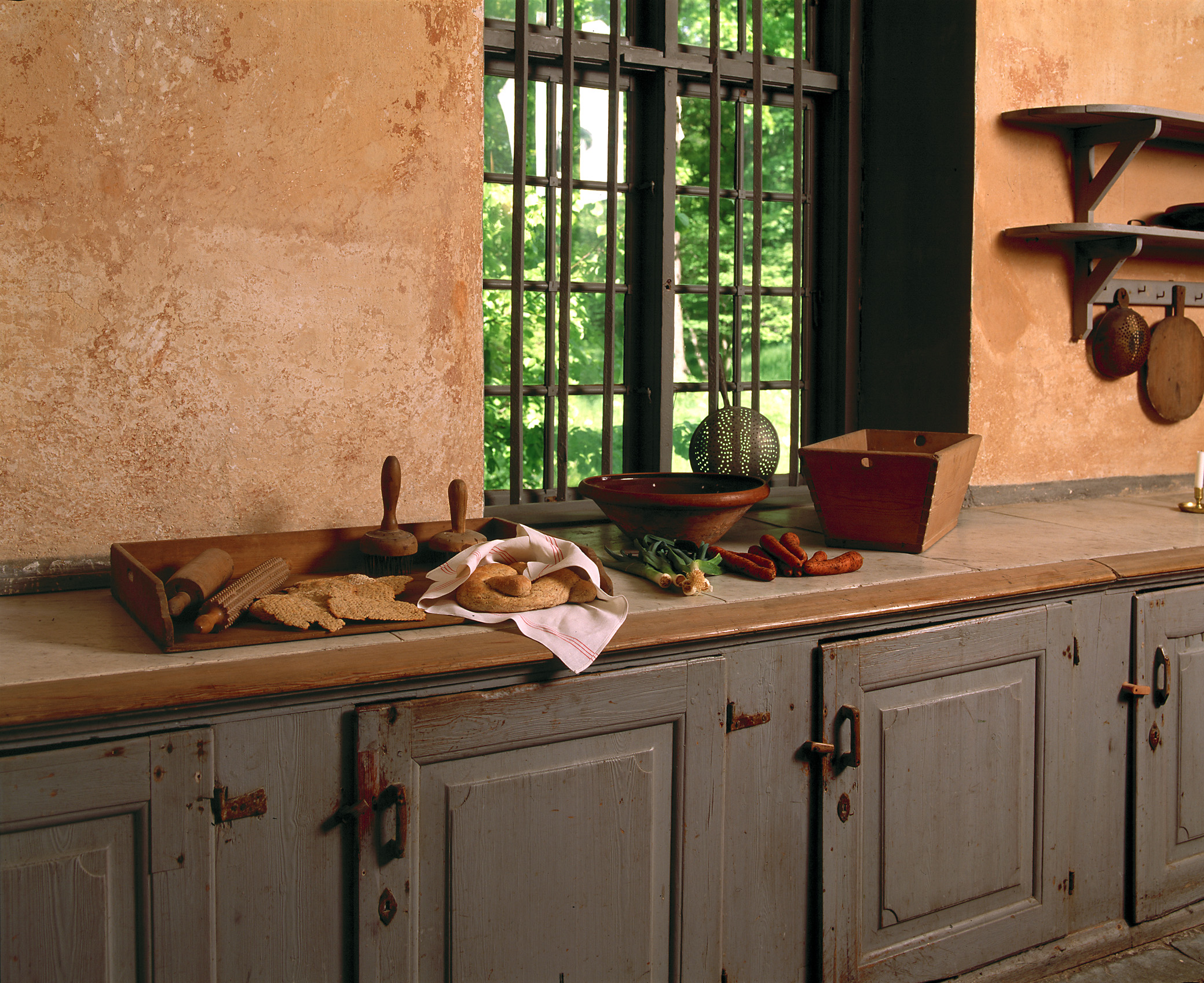
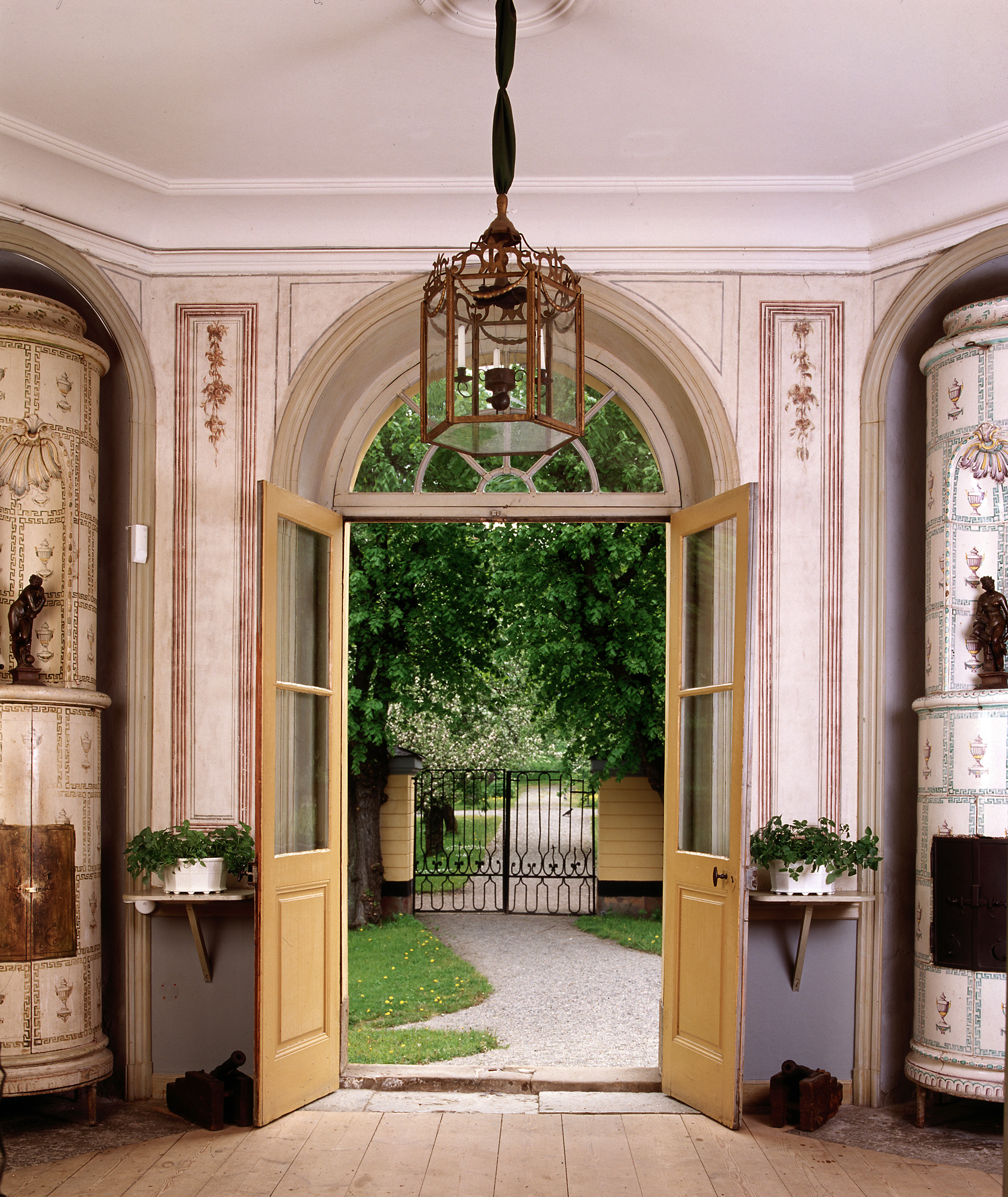
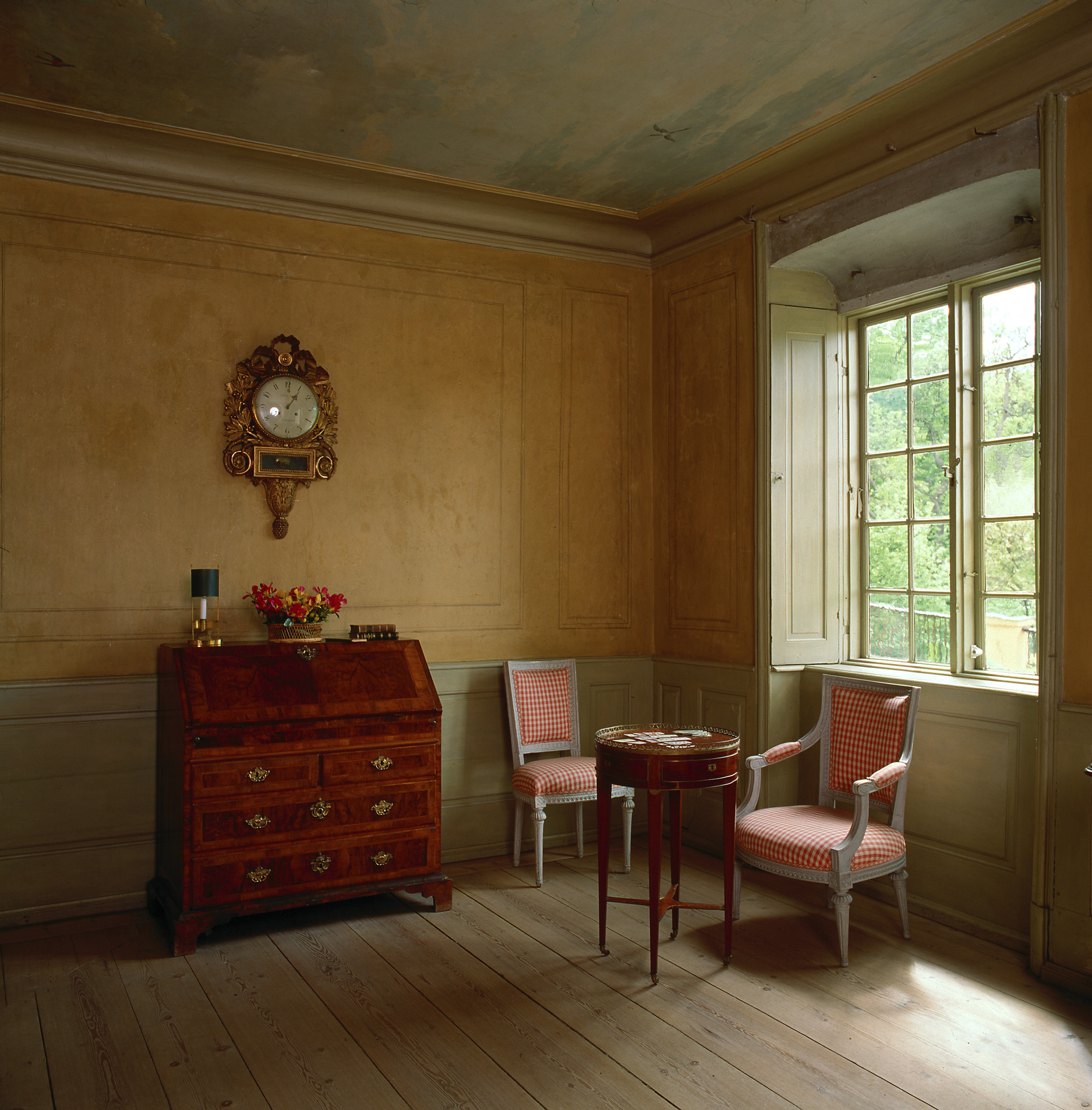
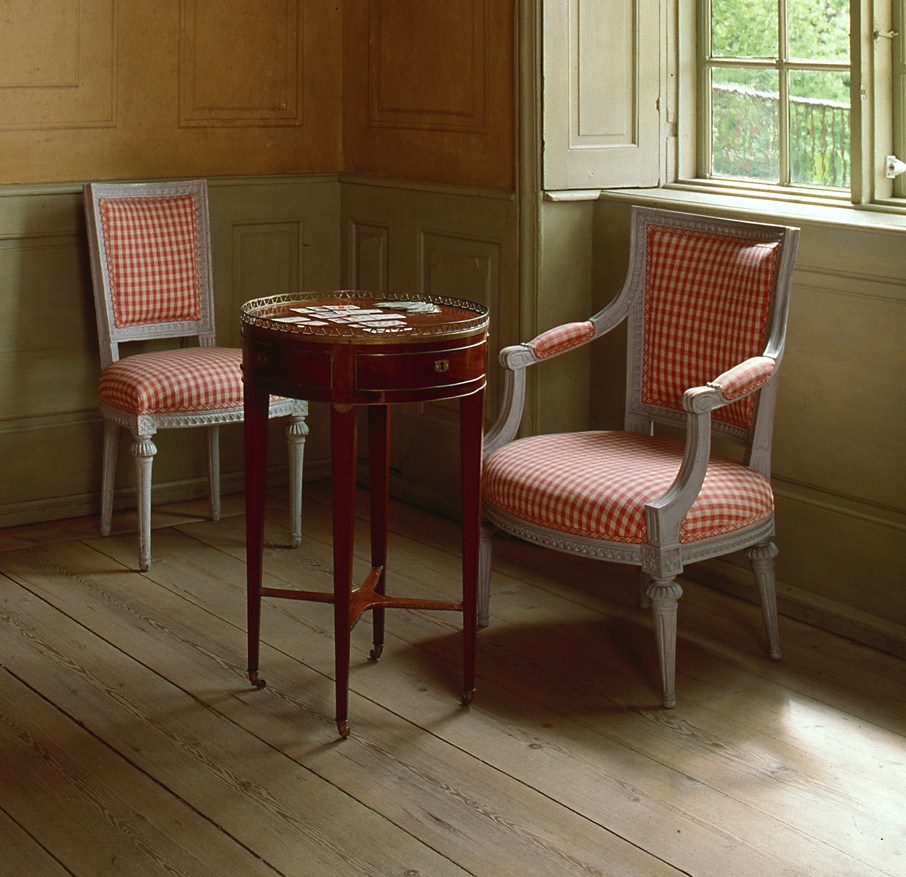
Swedish Interiors – Photographed By Photographer Joanna Holmgren
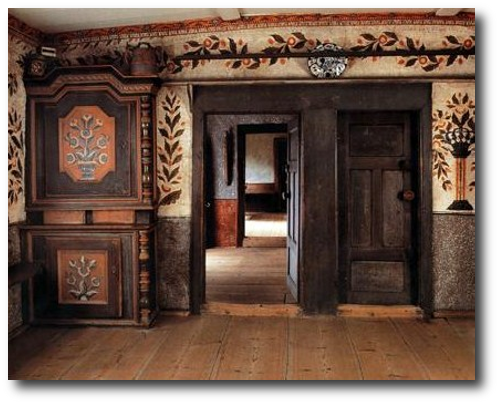
Swedish Interiors – Photographed By Photographer Joanna Holmgren
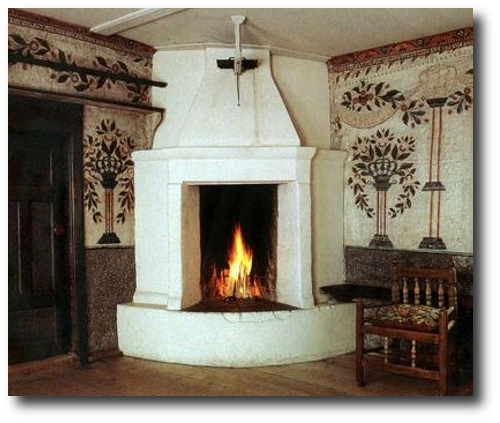
Swedish Interiors – Photographed By Photographer Joanna Holmgren
Sweden’s Manor Houses
Krapperup Castle Built in 1570 over the ruins of a 13th century stronghold; near Molle, Sweden From Larry Myhre’s Photstream
This Article “Inside Sweden’s Manor Houses” Published Nov/Dec-2002 By Dan Hofstadter in Departures
In a small rural province called Scania, three country estates define classic Swedish style.
It never occurred to me when I was living in Sweden, in the 1970s, that “Swedish style”—in furniture, interiors, and fabrics—might one day become popular in America. Swedish design, like Swedish humor, has a certain restraint, a quiet wit, that I would have thought lost on outsiders.
Yet classic Swedish design—and I don’t mean the 1950s masterpieces of Gunnar Asplund and Carl Malmsten or the Ikea explosion of the ’90s, but the checked-fabric side chairs and spindle-backed settees of 250 years ago—is experiencing a great deal of international attention these days. Shops showcasing Swedish antiques have recently opened in London, Paris, and New York, and decorating magazines seem obsessed with Swedish furnishings. The most obvious explanation is that 18th- and early-19th-century Swedish furniture, in its spareness and rectilinearity, fits in quite well with modern furniture; but there’s certainly more to it than that.
There is, I think, a real similarity between 18th-century Swedish and contemporary American taste, a psychological affinity that transcends history and geography and owes much, I would argue, to the ancestral Protestant craving for paring down, for simplicity. Many of America’s foremost furniture creators, from the Shakers through Gustave Stickley and the Eameses, have stressed economy, availability, and clean, well-defined lines. As it happens, these are also typical features of the Swedish interior.
Classic Swedish design reaches its apogee in the royal palaces and aristocratic country houses of Sweden. As late as the 17th and 18th centuries, Sweden was a very poor country whose noble families were often hard-pressed to maintain even the barest semblance of elegance. Many of the landed gentry were really glorified farmers who kept a sharp eye on expenses and shunned ostentation as wasteful and irreligious. Yet these families also wanted to enhance their status, and as they enlarged and improved their arable acreage, as revenues expanded and their tastes grew more refined, they began to remodel and embellish their houses. Toward the late 18th century, a style of design appeared that was simple enough to be affordable and also fashionable enough to give tone to a country seat. This was the Neoclassical style, and its chief exponent was King Gustav III, who ruled from 1771 to 1792. Because he offered so much patronage to builders and designers, he, in effect, created a revolution in taste.
High-strung and aloof, reserving his deepest affection for the theater, Gustav wrote full-length dramas of his own, shocked the court by performing onstage, and built himself a superb little theater in Gripsholm Castle, near Stockholm; some of his courtiers complained he was confusing statecraft with stagecraft. Having made a trip to Paris as crown prince, he was also keenly interested in Neoclassical art and design; in 1883 he traveled to Italy, where he visited Pompeii, Herculaneum, and Paestum. From France and Italy Gustav brought back drawings, paintings, statues, models, and a highly trained painter-architect named Louis Jean Desprez. The so-called Gustavian Style, still greatly admired by art-conscious Swedes, is in fact the Swedish naturalization of what we call the Louis Seize Style.
Gustav commissioned many grand interiors for royal palaces in the Stockholm area, but his subjects couldn’t follow his example to the letter. Too expensive for most of the Swedish nobility, his preferences were translated into a simpler, more provincial visual syntax. What emerged was the intimate, companionable, and at times rather countrified look of Swedish style.
Read More of This Article “Inside Sweden’s Manor Houses” Published Nov/Dec-2002 By Dan Hofstadter in Departures
- Wrams Gunnarstorp Castle From ZTaxi On Flicker
- Övedskloster Hakan Dahlstrbm’s Photostream
- Krageholm Sweden Built 1720


Krapperup Castle Built in 1570 over the ruins of a 13th century stronghold; near Molle, Sweden From Larry Myhre’s Photstream

Krageholm Sweden Built 1720
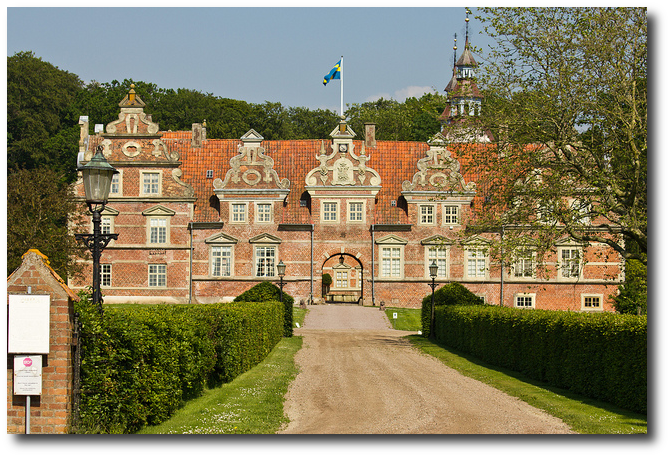

Wrams Gunnarstorp Castle From ZTaxi On Flicker






































