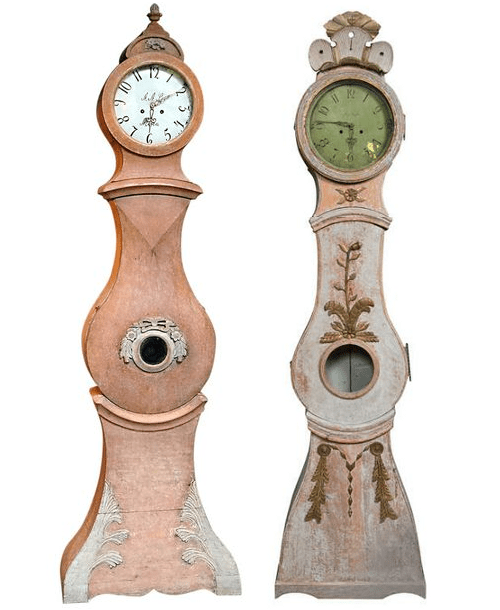Life In 17th Century Norway & Sweden
In the 17th and 18th centuries, the Nordic people had various desires and aspirations influenced by the social, economic, and cultural context of the time. Here are some of the most sought-after things during those centuries:
Wealth and Land: Accumulating wealth and owning land were significant aspirations for many people in the Nordic region. Land ownership represented social status, economic power, and provided opportunities for agricultural production and resource exploitation.
Trade and Commerce: Nordic countries, such as Sweden and Denmark, were engaged in international trade during this period. Merchants and traders sought to establish profitable connections with other European countries and expand their commercial ventures.
Access to New Goods: The growing trade networks allowed for the introduction of new and exotic goods into the Nordic region. People sought after luxury items like spices, silks, ceramics, and other commodities that were not readily available locally.
Education and Knowledge: The Enlightenment period in the 18th century brought an increased emphasis on education and the pursuit of knowledge. People sought access to education, particularly in fields like philosophy, science, and the arts.
Social Status and Prestige: Nobility and social hierarchy played an important role in the Nordic societies of the time. Many individuals desired to attain or maintain their noble status, associating themselves with the upper echelons of society.
Cultural and Intellectual Trends: The Nordic region saw an influx of ideas and cultural movements from other European countries. People sought to be part of these intellectual trends, embracing new philosophies, literary works, and artistic movements.
Scientific Advancements: The 17th and 18th centuries witnessed significant scientific discoveries and advancements. People were eager to access and learn about the latest scientific theories, particularly in fields such as astronomy, physics, and medicine.
Political Influence: As in other parts of Europe, power and political influence were highly sought after. Many individuals aspired to hold positions of authority, whether in local governance, regional politics, or the national administration.
It’s important to note that the desires and aspirations of individuals varied depending on their social class, occupation, and personal circumstances. These general themes provide a glimpse into the aspirations of people during the 17th and 18th centuries in the Nordic region.

18th Century Antique Swedish Rococo Tragsoffa | Vinterior
 Picture –thisivyhouse
Picture –thisivyhouse
Life In the 17th century Nordic countries
Daily Routine: People in the 17th century generally woke up early, as daylight was essential for most activities. They would begin their day with personal hygiene tasks like washing their face and hands, often using water from a basin. Due to limited sources of artificial lighting, the evening hours were typically dedicated to rest and sleep.
Work and Occupations: The majority of the population in the 17th century lived in rural areas and worked in agriculture. Farmers would tend to their crops and livestock, while women would engage in domestic tasks such as cooking, cleaning, and caring for children. In urban areas, people were involved in various trades and crafts. Merchants conducted business, artisans practiced their respective crafts, and apprentices learned skills from their masters.
Religion and Church: Religion played a significant role in daily life during the 17th century, particularly in Europe. Most people adhered to Christianity, and attending church services was a central part of their routine. Church buildings often served as community centers, where people gathered not only for religious activities but also for socializing and discussing local matters.
Education: Formal education was limited during this period, and literacy rates varied across regions. Wealthy families could afford tutors or send their children to private schools, while the lower classes often received basic education through informal means. Education focused on religious teachings, reading, writing, arithmetic, and vocational skills.
Entertainment and Recreation: In their leisure time, people in the 17th century engaged in various forms of entertainment. Popular recreational activities included playing games, such as cards, dice, and board games like chess or backgammon. Sports like archery, bowling, and tennis were also enjoyed. Social gatherings and events, such as dances, music performances, and theatrical plays, provided further amusement.
Art and Culture: The 17th century witnessed significant advancements in art and culture. Renowned artists like Rembrandt, Caravaggio, and Vermeer produced masterpieces during this period. Literature flourished with the works of influential writers like William Shakespeare, Miguel de Cervantes, and John Milton. Music, including compositions by composers like Johann Sebastian Bach and Antonio Vivaldi, also thrived.
Fashion and Dress: Clothing in the 17th century varied based on social class and occupation. Wealthy individuals wore garments made of fine fabrics and adorned with elaborate embellishments, while commoners dressed more simply. Fashion trends were influenced by the styles of the monarchy and the aristocracy, and clothing choices often reflected social status.
Food and Drink: The diet of people in the 17th century consisted of locally available food sources. Common staples included grains like wheat, barley, and oats, along with vegetables, legumes, and dairy products. Meat was primarily consumed by the wealthy, while the less affluent relied more on fish and poultry. Alcoholic beverages, such as beer and wine, were commonly consumed due to the limitations of safe water sources.
It’s important to note that the specifics of daily life in the 17th century varied greatly depending on the region and social circumstances.

The painted detail of a 18th Century Swedish Gustavian Chest – 1st Dibs


Antique Swedish Furniture

Swedish 18th Century Gustavian Clock with Original Paint – averydash.com/
Mora Clock in Original Salmon Paint Found on 1stdibs.com
Swedish Tall Case Clock, ca.1780-1800 Found on 1stdibs.com
19th Century Swedish Orange Painted Wooden Clock Found on 1stdibs.com
Gustavian Style Found on houzz.com
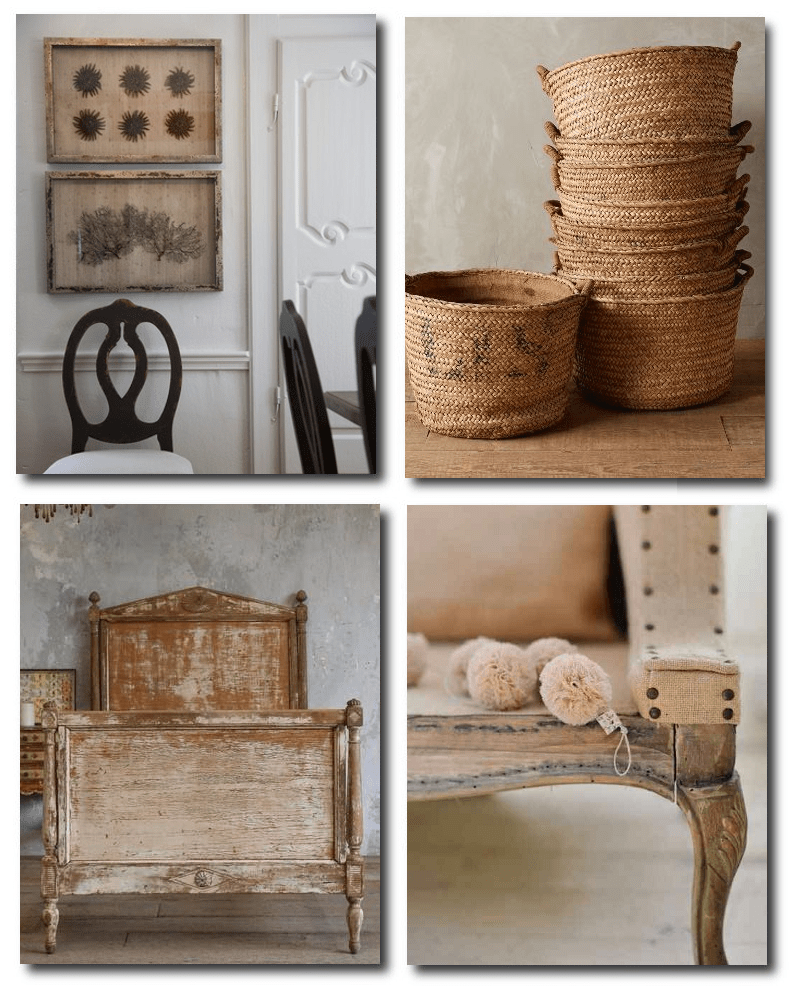
Harvest Basket, Found on anthropologie.com
Directoire Bed, Found on eloquenceinc.com
De-constructed Chair – Found on inspired-design.tumblr.com
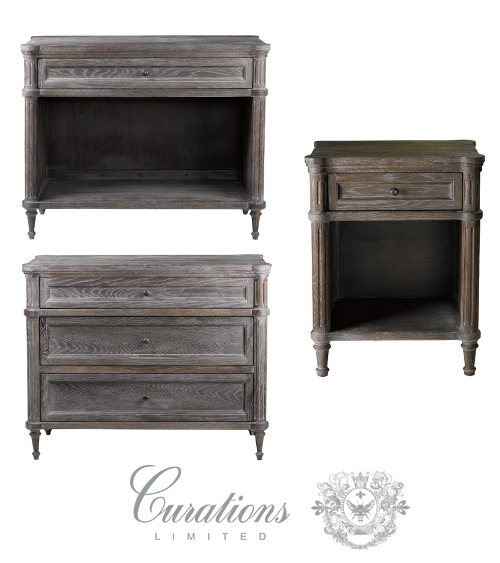 Alden Furniture Collections- Curations Limited
Alden Furniture Collections- Curations Limited
Vineyard Stripe Rug Ballard Designs
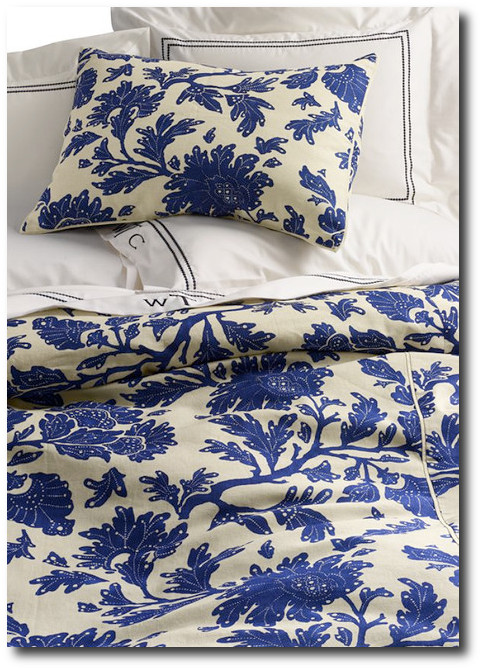
Harbor Springs Floral Duvet Cover, Lands End
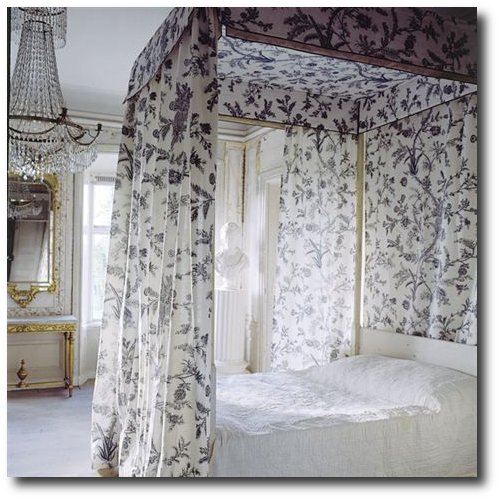
Buy Authentic Historical Textiles online at Ljungbergs Factory
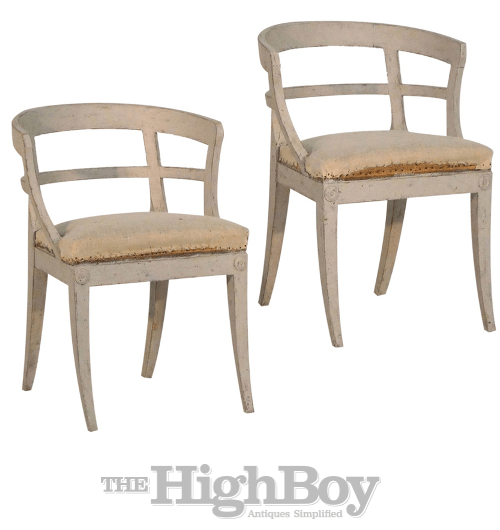 Pair of Swedish Sulla chairs with curved and open H-form backs, with original upholstery raised on splayed legs.- Highboy Antiques
Pair of Swedish Sulla chairs with curved and open H-form backs, with original upholstery raised on splayed legs.- Highboy Antiques

An antique looking mailbox – Amazon

A mailbox with a blue distressed finish – Amazon


Mid 19th Century Painted Water Carrier – debenhamantiques
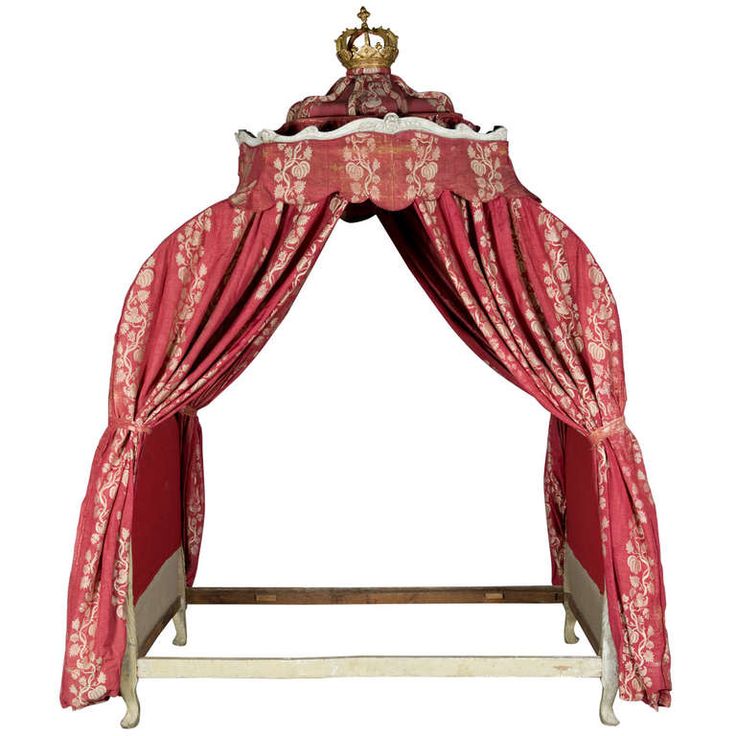
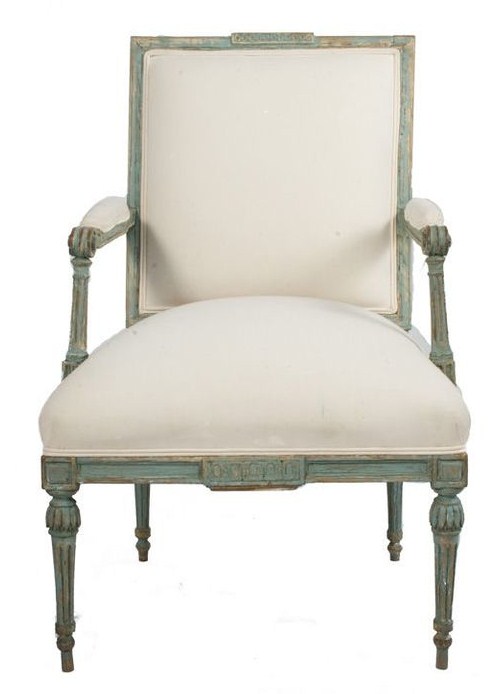








 decorativecollective.com
decorativecollective.com